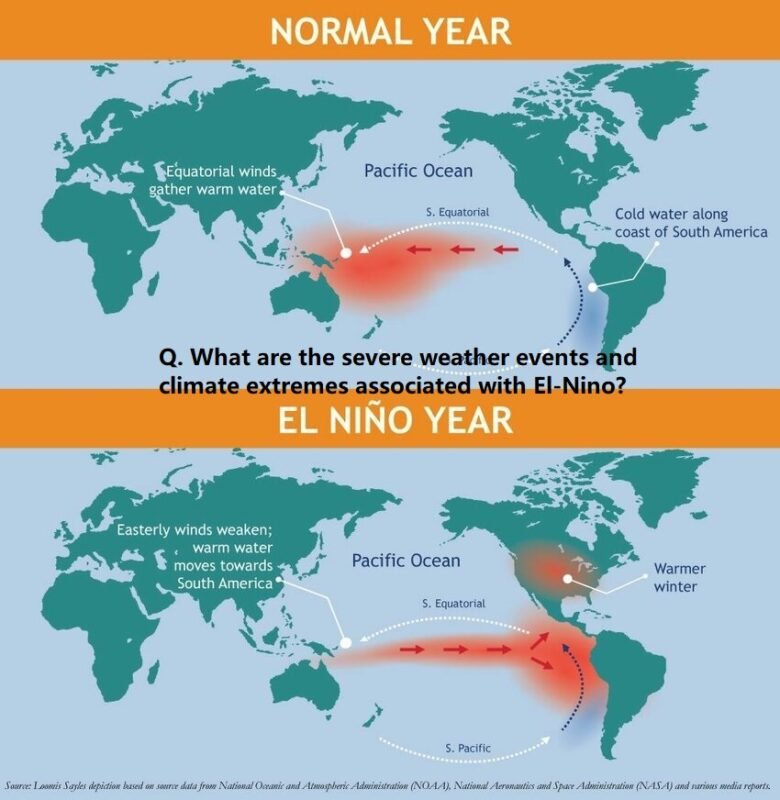
El Niño, a climatic phenomenon characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, has significant impacts on global weather patterns. These impacts result in various severe weather events and climate extremes. Here are some of the primary weather and climatic effects associated with El Niño:
Weather Events and Climate Extremes Associated with El-Niño
1. Droughts
- Australia: El Niño often leads to severe drought conditions in Australia, particularly in the eastern and northern regions, due to reduced rainfall.
- Southeast Asia: Countries like Indonesia and the Philippines experience drought, which can lead to water shortages and agricultural losses.
- India: The Indian subcontinent, especially during the summer monsoon season, can experience below-average rainfall, leading to drought conditions and impacting agriculture.
2. Flooding
- South America: Countries on the western coast, such as Peru and Ecuador, often experience heavy rainfall and severe flooding due to El Niño.
- Southern United States: El Niño can lead to increased rainfall and flooding in the southern parts of the United States, including California and the Gulf Coast.
3. Storms and Cyclones
- Pacific Hurricanes: There is often an increase in the frequency and intensity of hurricanes in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean during El Niño events.
- Atlantic Hurricanes: Conversely, the Atlantic hurricane season tends to be less active during El Niño due to increased wind shear, which inhibits storm formation.
4. Heatwaves
- Global Temperatures: El Niño is associated with higher global average temperatures, contributing to more frequent and intense heatwaves in various parts of the world.
- Western United States: El Niño can exacerbate heatwave conditions in the western United States, leading to extreme temperatures and increased risk of wildfires.
5. Wildfires
- Australia and Southeast Asia: The dry conditions caused by El Niño can lead to an increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in these regions.
- Western United States: Enhanced drought and heatwave conditions contribute to a higher incidence of wildfires.
6. Disruption of Marine Ecosystems
- Coral Bleaching: The warming of ocean waters during El Niño can lead to widespread coral bleaching, particularly in regions like the Great Barrier Reef.
- Fisheries: The shift in ocean currents and temperatures can disrupt marine food chains, impacting fisheries and leading to declines in fish populations.
Global Impact
- Food Security: Droughts and floods can significantly impact agricultural productivity, leading to food shortages and higher prices in affected regions.
- Health: Increased heatwaves and changes in precipitation patterns can exacerbate health issues, including heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems due to wildfires, and the spread of waterborne diseases.
- Economic Losses: Severe weather events associated with El Niño can lead to substantial economic losses due to damage to infrastructure, loss of agricultural output, and increased costs for disaster response and recovery.
Summary
El Niño’s influence on global weather patterns results in a wide range of severe weather events and climate extremes, including droughts, floods, storms, heatwaves, wildfires, and marine ecosystem disruptions. The impacts vary by region, but the overall effect is a significant alteration of normal weather patterns, often leading to substantial environmental, economic, and social consequences.