2024 GS P1 Solution, PYQs Solution
Q.4. Discuss the impacts of Globalization on Indian society.
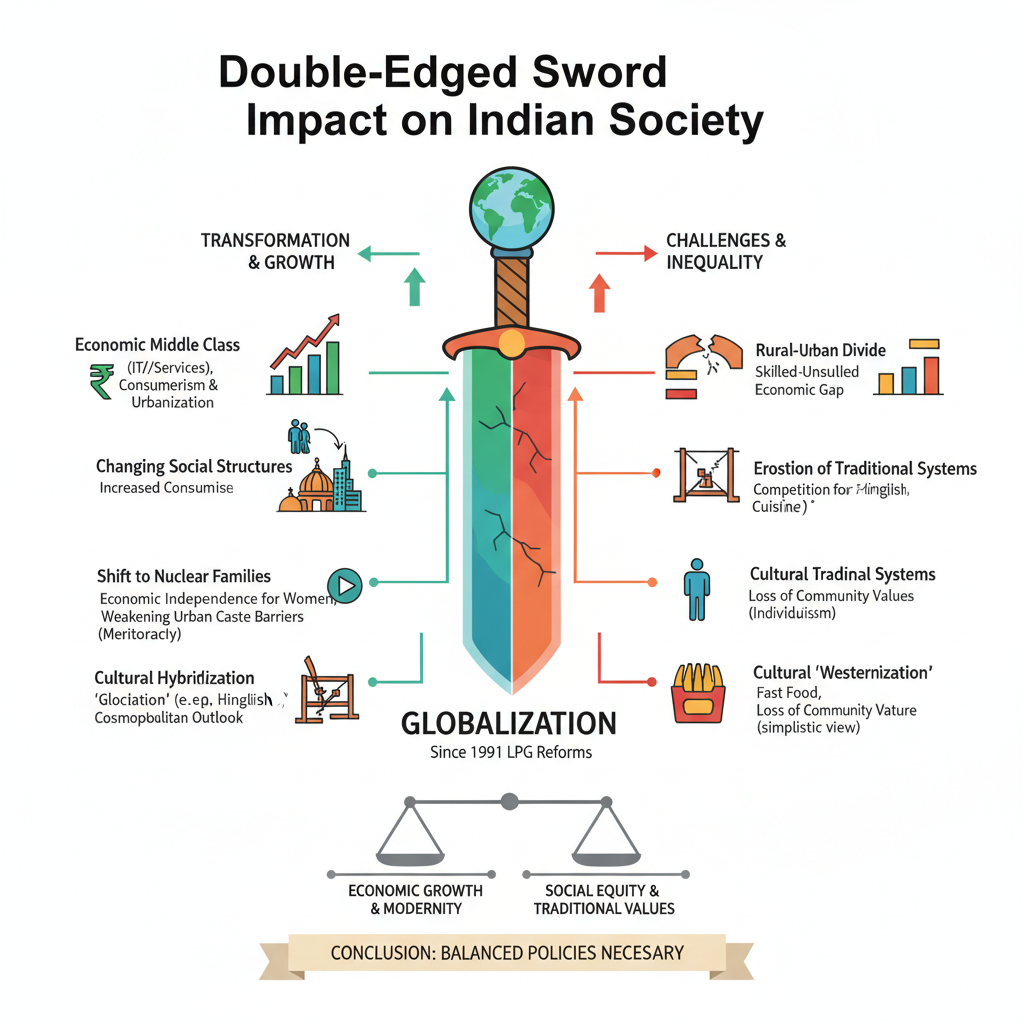
Globalization, particularly since the 1991 LPG reforms, signifies India’s increased integration with the world economy and culture. This process has had profound and multidimensional impacts on Indian society, affecting its economy, culture, and social structures.
The key impacts are:
- Economic Transformation: It created a new, aspirant middle class through the growth of the IT, service, and BPO sectors. This led to increased consumerism and rapid urbanization.
- Changing Social Structures: It accelerated the shift from traditional joint families to nuclear families. Globalization has also been a major factor in enhancing the economic independence and social mobility of women.
- Widening Inequality: The benefits have been unevenly distributed, aggravating the rural-urban divide and increasing the economic gap between the skilled and the unskilled.
- Cultural Hybridization: While often perceived as “Westernization” (e.g., fast food, Western attire), it has also led to “glocalization,” where global trends are adapted to local tastes (e.g., ‘Hinglish’, fusion cuisine), fostering a cosmopolitan outlook.
- Erosion of Traditional Systems: It has challenged traditional livelihoods, especially small-scale and cottage industries, which face competition from foreign goods. Socially, it has promoted individualism over community values.
- Dilution of Social Hierarchies: In urban and corporate settings, globalization has weakened traditional caste barriers by promoting meritocracy, though these structures remain entrenched in rural areas.
In conclusion, globalization has acted as a double-edged sword for Indian society. While it has driven economic growth and modernity, it has simultaneously posed significant challenges to social equity and traditional values, necessitating balanced policies.