AWIP, Internal Security
Q. How have India’s government initiatives and technological advancements addressed the complex challenges posed by its diverse and extensive border regions? What are the implications of border management for national security and development?
India’s government initiatives and technological advancements have been instrumental in addressing the complex challenges posed by its diverse and extensive border regions. These challenges range from territorial disputes and infiltration by hostile elements to issues related to the welfare of border communities. The implications of border management for national security and development are profound and multifaceted.
Key challenges in managing India’s border
- Long and diverse borders:
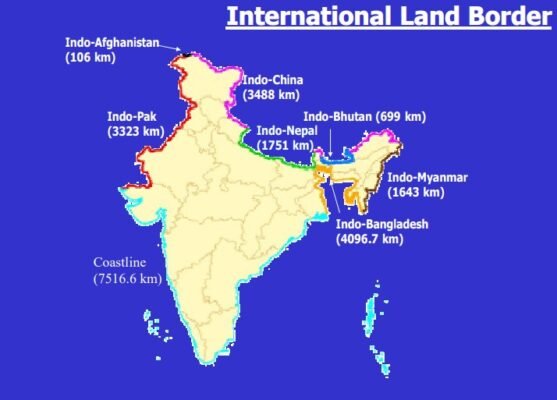 India has 15,106.7 Km of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 Km including island territories. The length of our land borders with neighbouring countries is as under:
India has 15,106.7 Km of land border and a coastline of 7,516.6 Km including island territories. The length of our land borders with neighbouring countries is as under:
|
Name of the country |
Length of the border (in Km) |
|
Bangladesh |
4,096.7 |
|
China |
3,488 |
|
Pakistan |
3,323 |
|
Nepal |
1,751 |
|
Myanmar |
1,643 |
|
Bhutan |
699 |
| Afghanistan |
106 |
| Total |
15,106.7 |
2. Diverse terrain: The mountains, deserts, rivers, forests, and plains, each poses unique challenges for border surveillance and management.
3. Security threats: Infiltration by terrorist groups, especially along the Pakistan and Myanmar border.
4. Smuggling and Trafficking: Illegal trade in arms, drugs, Wildlife animals, endemic and rare species, cattle & human trafficking.
5. FICN (Fake Indian Currency Notes), which promotes money laundering and supports organized crimes and terrorist funding.
6. Human & Resource constraints: A challenging task to ensure sufficient deployment of border security personnel along the borders.
7. Legal and diplomatic issues: Ongoing territorial disputes with China and Pakistan mandates maintaining effective diplomatic channels to manage and resolve border issues.
8. Infrastructure gaps: Inadequate infra (Road, Rail, Air connectivity) in remote border areas, affecting both security and development.
Government Initiatives
- Border Infrastructure Development: The Indian government has prioritized the development of infrastructure in border areas. This includes the construction of roads, bridges, and tunnels to improve connectivity and mobility. Projects like the Bharatmala Pariyojana and the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) are crucial in this regard. e.g., DS-DBO (Darbuk- Shyok- Daulat Beg Oldi) Road, Laddakh near China border.
- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs): To facilitate trade and travel, India has established ICPs at key border points. These are equipped with state-of-the-art facilities for customs, immigration, and security checks, thus enhancing the efficiency and security of cross-border movement.
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): This programme aims to meet the special development needs of people living in remote and inaccessible areas situated near the international border. It focuses on infrastructure development, health, education, and livelihood initiatives. e.g., Atul tunnel, Himachal Pradesh, all-weather connectivity between Manali and Leh, crucial for military and civilian movement. Sela Tunnel, Arunachal Pradesh, improving connectivity to Tawang region near China border. Kartarpur corridor, Punjab, facilitates visa free access for Indian pilgrimage to the Gurudwara Darbar Sahib in Pakistan.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS): It is an initiative that employs smart fencing with technologies like thermal imagers, infrared and laser-based intruder alarms, aerostats for aerial surveillance, ground sensors, floodlighting and enhancing border security through better infra (road, rail, air connectivity) to secure India’s borders.
- Defense Budget: India’s Defence Budget for FY 2024-25 is Rs 6,21,540.85 crore, 13.04% of the total Union Budget, reflecting a 4.72% increase from FY 2023-24. The budget emphasizes self-reliance and exports, with a significant portion allocated to capital expenditure (Rs 1.72 lakh crore) for modernizing the armed forces and promoting ‘Make in India’. Key investments include aircraft, submarines, and missile systems. Enhanced revenue expenditure supports operational readiness, while pension and welfare schemes for ex-servicemen see increased funding. Border infrastructure and Indian Coast Guard allocations rise to address strategic needs and emerging challenges. The DRDO budget also increases to boost defense innovation and technology.
Technological Advancements
- Surveillance Systems: India has deployed advanced surveillance systems, including drones, UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), and satellite imagery, to monitor border activities. These technologies help in real-time monitoring and quick response to any infiltration attempts.
- Communication Networks: Improved communication networks ensure seamless coordination between various border management agencies. Secure and reliable communication systems are critical for effective surveillance and rapid mobilization of forces.
- GIS and Remote Sensing: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies are used for mapping and monitoring border areas. These technologies assist in terrain analysis, planning of infrastructure projects, and management of natural resources.
- Cybersecurity Measures: With increasing digital threats, cybersecurity measures have been enhanced to protect sensitive information and communication networks involved in border management.
Implications for National Security
- Enhanced Security: Improved border management significantly enhances national security by preventing illegal infiltration, smuggling, and potential terrorist activities. The deployment of advanced surveillance and monitoring systems acts as a strong deterrent against hostile elements.
- Strategic Advantage: Better infrastructure and technological capabilities along the border provide a strategic advantage in terms of rapid deployment and mobilization of defense forces. This is crucial in case of any border skirmish or conflict.
- Intelligence Gathering: Technological advancements facilitate better intelligence gathering and analysis, enabling proactive measures against potential threats. This also helps in maintaining peace and stability in the region.
Implications for Development
- Economic Growth: Improved infrastructure and connectivity in border areas boost trade and economic activities. This not only benefits the local population but also enhances overall economic growth by opening up new markets and trade routes.
- Social Development: Government initiatives focused on education, healthcare, and livelihood in border areas contribute to the social development of these regions. This helps in integrating border communities into the mainstream and improving their quality of life.
- Disaster Management: Advanced technologies and infrastructure also play a critical role in disaster management. Improved communication and transport networks facilitate timely response and relief operations during natural disasters.
In conclusion, India’s comprehensive approach to border management, combining government initiatives and technological advancements, addresses the complex challenges of its diverse and extensive border regions. These measures not only bolster national security but also contribute significantly to the socio-economic development of border areas.


