Disaster Management, UPSC
Q.7. Dam failures are always catastrophic, especially on the downstream side, resulting in a colossal loss of life and property. Analyze the various causes of dam failures. Give two examples of large dam failures. [UPSC 2023 GS P-3]
Dam failures can have devastating consequences, affecting lives, property, and the environment. Let’s explore the causes of dam failures and highlight two significant examples:
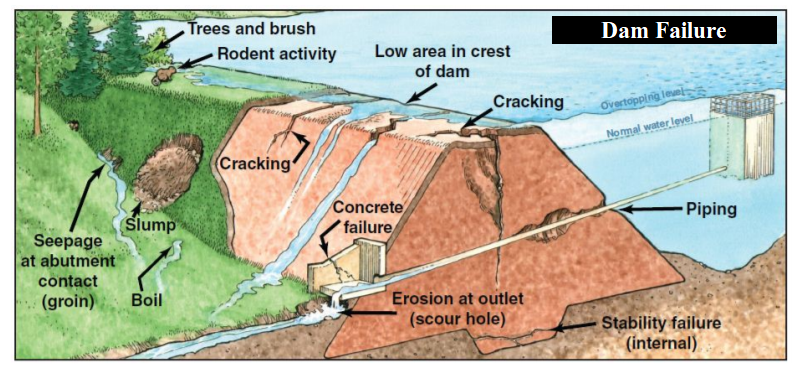
Causes of Dam Failures:
- Overtopping:
- Description: Overtopping occurs when water spills over the top of a dam, often due to inadequate spillway design, debris blockage, or settlement of the dam crest.
- Impact: It is a common precursor to dam failure, accounting for approximately 34% of all US dam failures.
- Foundation Defects:
- Description: Foundation defects include settlement and slope instability. These issues weaken the dam’s structural integrity.
- Impact: Foundation-related problems cause about 30% of all dam failures.
- Seepage and Internal Erosion:
- Description: Poor foundation conditions, seepage, and internal erosion weaken the dam structure.
- Impact: If not addressed, these factors can lead to catastrophic failure.
- Spillway Design Errors:
- Description: Inadequate spillway design can result in insufficient water discharge during floods.
- Impact: Insufficient spillway capacity can lead to overtopping and dam failure.
- Structural Issues:
- Description: Flaws in dam construction materials or techniques can compromise stability.
- Impact: Sub-standard materials contribute to dam failures.
Examples of Large Dam Failures:
- Machchhu Dam Failure (1979):
- Location: Morbi, Gujarat, India.
- Cause: Excessive rainfall.
- Impact: Due to mechanical failure, the gates of Machchhu – II dam malfunctioned. This resulted in heavy flooding in Morbi, leading to the loss of 2000 lives and extensive damage to infrastructure. It remains one of the worst dam failures in India.
- Uttarakhand Dam Disaster (2021):
-
- Location: Chamoli, Uttarakhand, India.
- Cause: A devastating glacial event and dam collapse.
- Impact: The Rishiganga hydroelectric power project was almost entirely buried under mud and ice, and another dam project on the Dhauliganga River was severely damaged.
- Teton Dam (1976):
- Location: Idaho, USA.
- Cause: Poor foundation conditions and inadequate spillway design.
- Impact: The dam collapsed, resulting in significant loss of life and property damage.
- Banqiao Dam (1975):
- Location: Henan, China.
- Cause: Excessive rain and flooding.
- Impact: The catastrophic failure of the Banqiao Dam during Typhoon Nina led to immense devastation and loss of life.
In summary, these incidents highlight the importance of robust dam design, maintenance, and disaster preparedness to prevent such catastrophic events. Understanding the causes of dam failures is crucial for preventing future disasters and ensuring public safety. Proper maintenance, regulatory oversight, and risk mitigation are essential to minimize the risks associated with dam failures.