Indian Polity & The Constitution of India
Latest Posts
Q.15. Discuss India as a secular state and compare with the secular principles of the US constitution. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
India as a Secular State: India is a secular state as outlined in its Constitution, [...]
read moreQ.14. Explain the reasons for the growth of public interest litigation in India. As a result of it, has the Indian Supreme Court emerged as the world’s most powerful judiciary? [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
Reasons for the Growth of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in India: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) [...]
read moreQ.13. What changes has the Union Government recently introduced in the domain of Centre-State relations? Suggest measures to be adopted to build the trust between the centre and the States and for strengthening federalism. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
In recent times, the Union Government of India has introduced several changes and initiatives that [...]
read moreQ.12. Right to privacy is intrinsic to life and personal liberty and is inherently protected under Article 21 of the constitution. Explain. In this reference discuss the law relating to DNA testing of child in the womb to establish its paternity. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
Right to Privacy and Article 21 of the Constitution The Right to Privacy is recognized [...]
read moreQ.11. What are the aims and objects of recently passed and enforced, The Public Examination (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024? Whether University/State Education Board examinations, too, are covered under the Act? [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
In recent years, there have been numerous instances of question paper leaks in recruitment exams [...]
read moreQ.5. Analyse the role of local bodies in providing good governance at local level and bring out the pros and cons merging the rural local bodies with the urban local bodies. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
Role of Local Bodies in Providing Good Governance at the Local Level Local bodies, both [...]
read moreQ.4. “The duty of the Comptroller and Auditor General is not merely to ensure the legality of expenditure but also its propriety.” Comment. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
The statement that “the duty of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) is not merely [...]
read moreQ. Pundit Jawahar Lal Nehru and B. R. Ambedkar did not include secularism in the Constitution. Why?
The absence of an explicit mention of “secularism” in the original Constitution of India can [...]
read moreOct
Q.3. “The growth of cabinet system has practically resulted in the marginalization of the parliamentary supremacy.” Elucidate. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
The statement that “the growth of the cabinet system has practically resulted in the marginalization [...]
read moreQ.2. Explain and distinguish between Lok Adalats and Arbitration Tribunals. Whether they entertain civil as well as criminal cases? [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
Lok Adalats and Arbitration Tribunals are both alternative dispute resolution (ADR) mechanisms in India, designed [...]
read moreOct
Q.1. Examine the need for electoral reforms as suggested by various committees with particular reference to “one nation – one election” principle. [UPSC 2024 GS P-2]
The need for electoral reforms in India has been widely acknowledged by various committees, experts, [...]
read moreSep
Q.3. To what extent, in your opinion, has the decentralization of power in India changed the governance landscape at the grassroots? [UPSC 2022 GS P-2]
Decentralization of power in India, especially through the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments (1992), has [...]
read moreQ.2. “Right of movement and residence throughout the territory of India are freely available to the Indian citizens, but these rights are not absolute.” Comment. [UPSC 2022 GS P-2]
The right of movement and residence throughout the territory of India is enshrined under Article [...]
read moreQ.1. “The most significant achievement of modern law in India is the constitutionalization of environmental problems by the Supreme Court.” Discuss this statement with the help of relevant case laws. [UPSC 2022 GS P-2]
The statement, “The most significant achievement of modern law in India is the constitutionalization of [...]
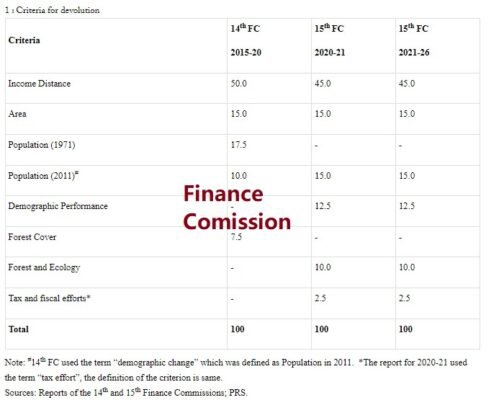
read moreQ. Describe the constitutional provisions regarding the Finance Commission of India and explain its functions.
The Finance Commission of India is a constitutional body established under Article 280 of the [...]
read moreJul
Q. Explain the discretionary powers of the President of India.
The President of India primarily functions as a ceremonial head of state with executive powers [...]
read moreQ. Critically examine the idea of “One Nation, One Election” in India.
The idea of “One Nation, One Election” in India proposes synchronizing the elections for the [...]
read moreQ. “Prime Minister is the nucleus of the Indian Political System.” Discuss.
The statement “Prime Minister is the nucleus of the Indian Political System” emphasizes the central [...]
read moreQ. What are the emerging issues raised by some states in India in the context of fiscal federalism? Express your view in this context.
Fiscal federalism in India, the financial relationship between the central and state governments, has been [...]
read moreJul
Q.5. Discuss the role of Presiding Officers of state legislatures in maintaining order and impartiality in conducting legislative work and in facilitating best democratic practices. [UPSC 2023 GS P-2]
The presiding officers of state legislatures, typically known as the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly [...]
read moreQ.4. Compare and contrast the British and Indian approaches to Parliamentary sovereignty. [UPSC 2023 GS P-2]
Parliamentary sovereignty, a cornerstone of the British constitutional framework, is interpreted and applied differently in [...]
read moreJun
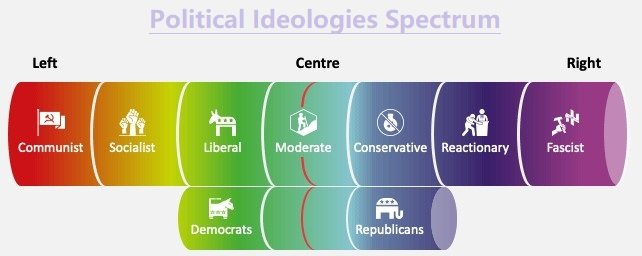
Q. What do you understand by the ‘left’ and the ‘right’ terminologies in politics? According to you, which ideology is better for the sustainable development of a democratic nation?
Understanding ‘Left’ and ‘Right’ Terminologies in Politics The ‘Left’ Ideological Foundations Economic Equality: Advocates for [...]
read moreJun
Q. Critically analyze the role of pressure groups in Indian political process? Do you think that in recent years, they have emerged as an important actor on Indian political landscape?
Role of Pressure Groups in the Indian Political Process Pressure groups, also known as interest [...]
read moreJun
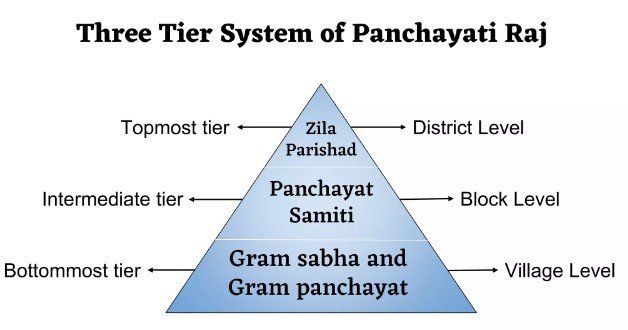
Q. Examine the autonomy and control over Panchayati Raj Institutions. What suggestions would you like to give to make them more effective, creative and receptive with special reference to Uttar Pradesh.
Examination of Autonomy and Control over Panchayati Raj Institutions Autonomy and Control: Legal and Constitutional [...]
read moreJun
Q. Describe the stages involved in the election process, from announcement to declaration of results.
Elections are fundamental to democracy, as they allow citizens to choose their representatives through voting. The [...]
read moreQ. Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India (ECI) in ensuring free and fair elections.
Election Commission of India (ECI) is a constitutional body that conducts and regulates elections in India. It has the power of [...]
read moreQ. How does the political participation of college students contribute to India’s democratic ethos? Discuss their activism, electoral engagement and ideological debates.
College is a breeding ground for future political leaders. Their participation in student unions and [...]
read moreJun
Q.2. Assess the role of National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) in rendering free legal aid in India.
The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) is a statutory body which was established under the Legal [...]
read moreJun
Q.3. “The states in India seem reluctant to empower urban local bodies both functionally and financially.” Comment. [UPSC 2023 GS P-2]
The statement reflects a significant challenge in the governance of urban areas in India. Despite [...]
read moreMay
Q.1. “Constitutionally guaranteed judicial independence is a prerequisite of democracy.” Comment. [UPSC 2023 GS P-2] “संवैधानिक रूप से न्यायिक स्वतंत्रता की गारंटी लोकतंत्र की एक पूर्व शर्त है|” टिप्पणी कीजिए|
The statement “Constitutionally guaranteed judicial independence is a prerequisite of democracy” underscores the fundamental role [...]
read more