AWIP, Indian Polity & The Constitution of India, News Analysis
Q. What do you understand by the ‘left’ and the ‘right’ terminologies in politics? According to you, which ideology is better for the sustainable development of a democratic nation?
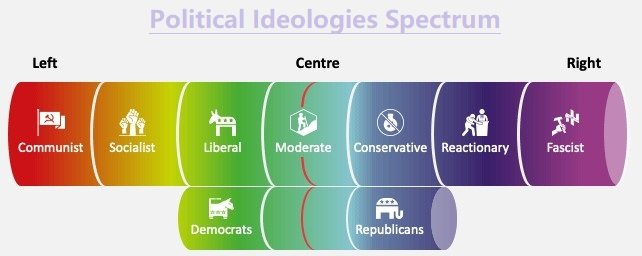
Understanding ‘Left’ and ‘Right’ Terminologies in Politics
The ‘Left’
Ideological Foundations
- Economic Equality: Advocates for reducing economic disparities through wealth redistribution, progressive taxation, and social welfare programs.
- Social Justice: Emphasizes social equality, minority rights, and policies aimed at reducing discrimination and promoting inclusivity.
- Government Intervention: Supports a significant role for government in the economy to regulate markets, provide public services, and ensure social security.
- Progressivism: Favors progressive social policies, including those related to education, healthcare, labor rights, and environmental protection.
Political Movements and Parties
- Examples include socialist and communist parties, as well as progressive and social democratic movements.
The ‘Right’
Ideological Foundations
- Economic Liberalism: Advocates for free-market capitalism, minimal government intervention in the economy, and the promotion of private enterprise.
- Individual Responsibility: Emphasizes personal responsibility, self-reliance, and the importance of individual freedoms.
- Traditional Values: Often supports traditional social norms and values, with a focus on preserving cultural and religious heritage.
- Limited Government: Prefers a smaller government, reducing bureaucratic control, and emphasizing private sector solutions to social and economic issues.
Political Movements and Parties
- Examples include conservative, liberal (in the classical sense), and right-wing populist parties.
Which Ideology is Better for Sustainable Development in a Democratic Nation?
The question of which ideology is better for sustainable development in a democratic nation is complex and depends on various factors, including the specific context of the nation, its socio-economic conditions, cultural values, and historical experiences. Both ideologies have strengths and weaknesses when it comes to sustainable development:
Strengths of the Left
- Social Equity: Emphasizes reducing inequality and ensuring that all citizens have access to basic needs such as healthcare, education, and social security. This can lead to a more inclusive society where everyone can contribute to and benefit from economic growth.
- Environmental Protection: Progressive policies often include strong measures to protect the environment, such as regulations on pollution and investment in renewable energy, which are crucial for long-term sustainability.
- Public Services: Strong public services provided by the government can ensure that all citizens have access to essential services, promoting social stability and overall well-being.
Strengths of the Right
- Economic Efficiency: Emphasizes free-market principles, which can drive innovation, efficiency, and economic growth. Private sector involvement can often lead to more efficient resource allocation and productivity.
- Personal Responsibility: Encourages individual initiative and entrepreneurship, which can lead to economic dynamism and job creation.
- Limited Government: Reducing the size of government and bureaucracy can lead to lower taxes and reduced regulatory burdens, potentially fostering a more business-friendly environment.
A Balanced Approach
For sustainable development in a democratic nation, a balanced approach that incorporates the strengths of both ideologies may be most effective. This would involve:
- Economic Growth with Equity: Combining market-driven economic growth with policies that ensure equitable distribution of resources and opportunities.
- Environmental Sustainability: Ensuring that economic development is environmentally sustainable, incorporating both regulatory measures and market-based solutions.
- Inclusive Policies: Implementing social policies that protect vulnerable populations and promote social justice while encouraging personal responsibility and innovation.
- Effective Governance: Striking a balance between efficient government intervention where necessary and allowing market mechanisms to operate where they are most effective.
Conclusion
No single ideology holds all the answers to the complex challenge of sustainable development. A pragmatic approach that leverages the strengths of both the left and the right, tailored to the specific needs and context of the nation, is likely to be the most effective for achieving sustainable development in a democratic nation. This approach ensures economic growth, social equity, environmental protection, and effective governance, ultimately leading to a more stable and prosperous society.